If you’ve ever experienced that uncomfortable burning sensation in your chest known as acid reflux, you know how important it is to find relief. But when should you take your symptoms more seriously and seek medical attention? This article will dive into the warning signs to watch for when it comes to acid reflux, helping you understand when it’s time to see a doctor. From persistent heartburn to difficulty swallowing, knowing these signs can help you stay proactive in managing your reflux and finding the right treatment. So, let’s get started and learn when it’s time to seek professional help for your acid reflux symptoms.
This image is property of www.gerdhelp.com.
Overview of Acid Reflux
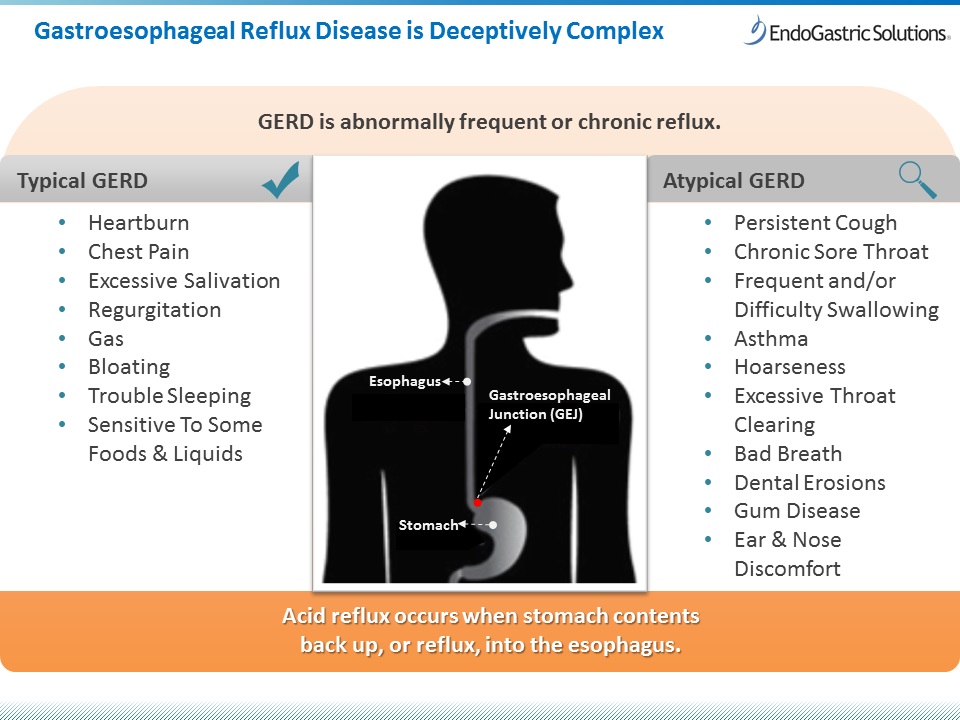
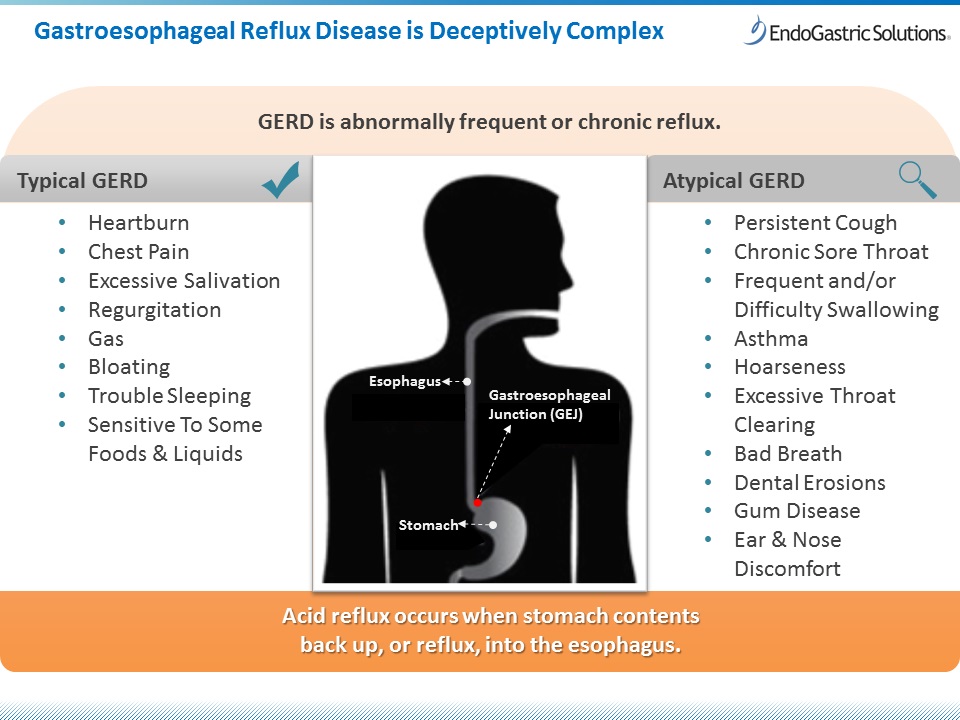
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a common digestive disorder that occurs when the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This can cause a variety of symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, a sour taste in the mouth, and difficulty swallowing. While occasional acid reflux is normal, frequent episodes can be a cause for concern. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for acid reflux is important in managing this condition effectively.
Understanding Acid Reflux
Acid reflux occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) – the ring of muscle between the esophagus and stomach – becomes weak or relaxes at the wrong times. This allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. Certain factors can contribute to the development of acid reflux, such as obesity, smoking, pregnancy, hiatal hernia, and certain medical conditions.
Causes of Acid Reflux
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of acid reflux. These include:
- Diet: Consuming certain trigger foods like citrus fruits, spicy foods, fatty or fried foods, chocolate, and caffeine can increase the risk of acid reflux.
- Lifestyle habits: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can weaken the LES and increase the likelihood of acid reflux.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the abdomen during pregnancy can lead to acid reflux.
- Medications: Some medications like certain pain relievers, sedatives, and blood pressure medications can weaken the LES and cause acid reflux.
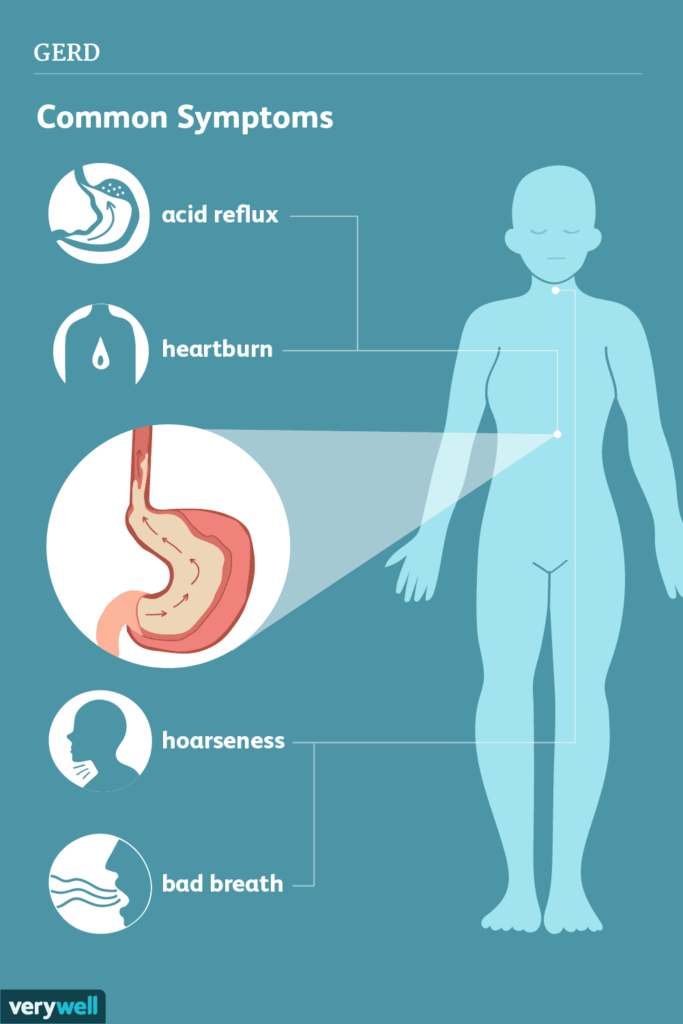
Symptoms of Acid Reflux
The symptoms of acid reflux can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating or when lying down.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of acid or food coming back up into the throat or mouth.
- Sour or bitter taste: A persistent sour or bitter taste in the mouth, especially after eating.
- Difficulty swallowing: A feeling of food being stuck in the throat or chest.
- Chronic cough: A persistent cough that is often worse at night.
- Hoarseness: Changes in the voice, such as a hoarse or raspy voice.
It is important to note that not all individuals with acid reflux will experience these symptoms. Some may only experience mild symptoms, while others may have more severe manifestations.

This image is property of lirp.cdn-website.com.
Common Treatments for Acid Reflux
When it comes to treating acid reflux, there are several approaches that can be taken depending on the severity of the symptoms. These treatments can include lifestyle changes, over-the-counter (OTC) medications, prescription medications, and in some cases, surgical options.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain modifications to your lifestyle can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the frequency of acid reflux episodes. Some lifestyle changes that may be beneficial include:
- Avoiding trigger foods: Identifying and avoiding foods that trigger acid reflux can help manage symptoms. This may include staying away from spicy foods, citrus fruits, greasy or fatty foods, and caffeine.
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals: Consuming smaller meals throughout the day instead of larger meals can help reduce the pressure on the stomach and decrease the likelihood of acid reflux.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Losing excess weight can alleviate pressure on the abdomen and reduce the occurrence of acid reflux.
- Avoiding lying down after meals: Waiting at least two to three hours after eating before lying down can help prevent acid reflux.
- Elevating the head of the bed: Raising the head of the bed by using wedges or blocks can help keep stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus during sleep.
OTC Medications
Over-the-counter medications can provide relief for mild to moderate acid reflux symptoms. Antacids, such as Tums or Rolaids, can help neutralize stomach acid and provide temporary relief. Other OTC medications, such as H2 blockers (e.g., ranitidine or famotidine) and proton pump inhibitors (e.g., omeprazole or lansoprazole), can help reduce the production of stomach acid and provide longer-lasting relief.
Prescription Medications
For individuals with more severe or persistent acid reflux, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications. These can include prescription-strength proton pump inhibitors, foam barriers, or prokinetics. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and prescription of medications, as they will consider individual factors and potential interactions with other medications.
Surgical Options
In cases where lifestyle modifications and medications do not effectively manage acid reflux, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgical options for acid reflux include fundoplication, a procedure where the upper part of the stomach is wrapped around the LES to strengthen it, and endoscopic procedures, such as Stretta or LINX, which use sutures or magnetic beads to reinforce the LES. These surgical interventions are typically reserved for individuals with severe acid reflux or complications.
When to Self-Treat Acid Reflux
Not all cases of acid reflux require immediate medical attention. Mild and occasional symptoms can often be managed at home with self-care measures. However, it is important to know when self-treatment is appropriate and when it is necessary to seek medical help.
Mild and Occasional Symptoms
If you experience mild and infrequent symptoms of acid reflux, self-treatment may be sufficient. This can include making lifestyle changes, such as avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, and avoiding lying down after eating. Additionally, over-the-counter antacids can provide temporary relief for occasional heartburn.
Managing Acid Reflux with Lifestyle Changes
When symptoms of acid reflux are manageable through lifestyle changes alone, self-treatment can be effective. However, if symptoms persist despite these modifications or worsen over time, it is important to consider seeking medical help.
Identifying Triggers and Avoiding Them
If you are able to identify specific trigger foods or behaviors that worsen your acid reflux symptoms, avoiding them can often alleviate the need for medical intervention. By keeping a food diary and tracking your symptoms, you can gain a better understanding of what triggers your acid reflux and modify your diet accordingly.
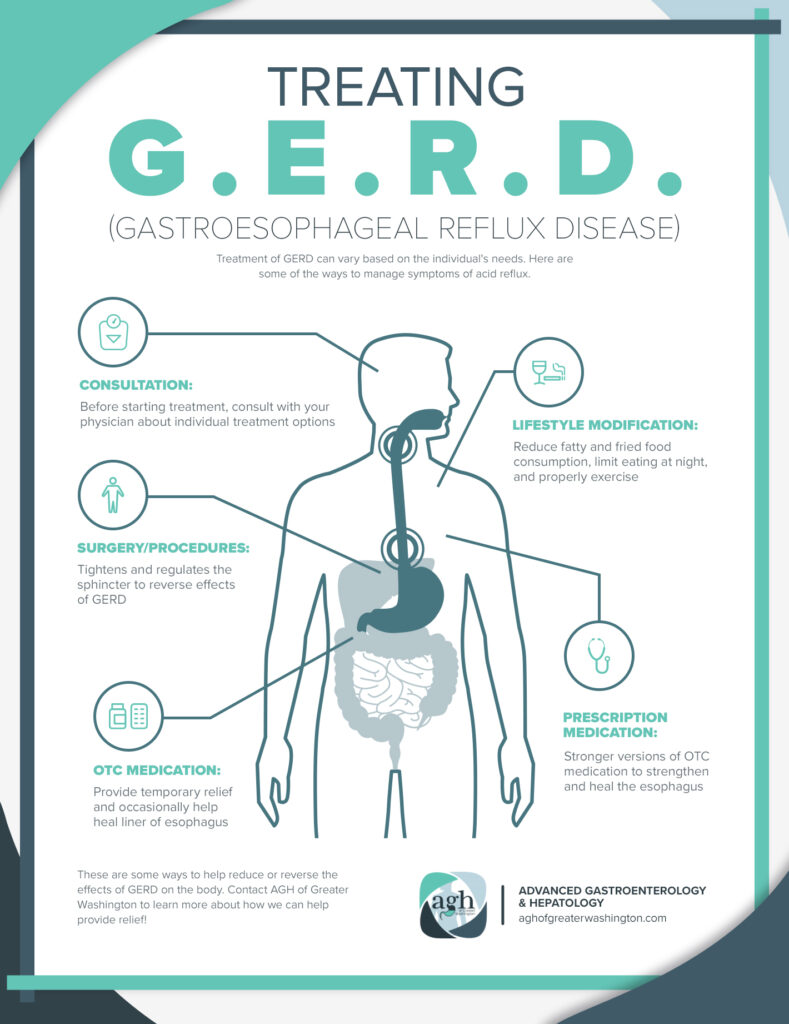
This image is property of aghofgreaterwashington.com.
Knowing When to Seek Medical Help
While self-treatment can be effective for mild and occasional acid reflux, there are certain warning signs that indicate the need for medical attention. These signs should not be ignored and prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional is recommended.
Frequency and Severity of Symptoms
If you experience frequent episodes of acid reflux or if your symptoms are becoming increasingly severe, it is advisable to see a doctor. Frequent heartburn, regurgitation, or difficulty swallowing can indicate underlying issues that require further evaluation.
Persistent Symptoms despite Lifestyle Changes
If you have made significant lifestyle modifications to manage your acid reflux but continue to experience persistent symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. This may indicate the need for stronger medications or further investigation into the underlying cause of your symptoms.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss can be a concerning symptom associated with acid reflux. If you have experienced significant weight loss without actively trying to lose weight, it is recommended to seek medical attention to rule out any serious underlying conditions.
Difficulty Swallowing or Painful Swallowing
If you experience difficulty or pain when swallowing, it could be a sign of complications related to acid reflux. These symptoms may indicate the presence of esophageal narrowing (stricture) or damage to the esophagus that requires medical evaluation.
Persistent Cough or Hoarseness
A persistent cough or hoarseness can be indicative of acid reflux affecting the throat and vocal cords. If these symptoms persist for an extended period or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional.
Chest Pain
While chest pain can have various causes, it is important not to disregard it when experiencing acid reflux symptoms. Chest pain that is severe, prolonged, or accompanied by other symptoms such as shortness of breath or arm pain may be indicative of something more serious and should be evaluated by a medical professional.
Severe Heartburn
If you experience severe or unrelenting heartburn that is not relieved by over-the-counter medications, it is advisable to seek medical attention. Severe heartburn can be a sign of more severe acid reflux or complications.
Worsening Symptoms
When symptoms worsen over time or become more frequent and intense, medical evaluation is recommended. Acid reflux that is progressively worsening can indicate the need for stronger medications or alternative treatment options.
Symptoms Interfering with Daily Life or Sleep
If acid reflux symptoms significantly interfere with your daily life, work, or sleep, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Chronic disruption caused by acid reflux can have a significant impact on quality of life and may require medical intervention.
Concerns about Esophageal Damage
If you have concerns about potential damage to your esophagus due to acid reflux or if you have a family history of esophageal conditions, it is crucial to seek medical advice. Regular monitoring and evaluation may be necessary to detect any complications or early signs of esophageal damage.
Diagnostic Tests for Acid Reflux
To accurately diagnose acid reflux and assess potential complications, healthcare providers may recommend various diagnostic tests. These tests can help determine the severity of acid reflux, assess the condition of the esophagus, and guide appropriate treatment options.
Upper Endoscopy
An upper endoscopy, also known as esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), involves the use of a flexible tube with a camera to visualize the inside of the esophagus, stomach, and upper small intestine. This allows the healthcare provider to assess the condition of the esophagus and identify any signs of damage or inflammation.
Esophageal pH Monitoring
Esophageal pH monitoring involves placing a small probe into the esophagus to measure the amount of acid present over a 24-hour period. This test helps determine the frequency of acid reflux episodes and the effectiveness of treatment.
Esophageal Manometry
Esophageal manometry measures the pressure and movement of the esophagus. This test helps assess the strength and coordination of the muscles involved in swallowing and can identify any abnormalities that may contribute to acid reflux.
X-ray and Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays or barium swallow may be used to evaluate the esophagus and identify any structural abnormalities or complications related to acid reflux.
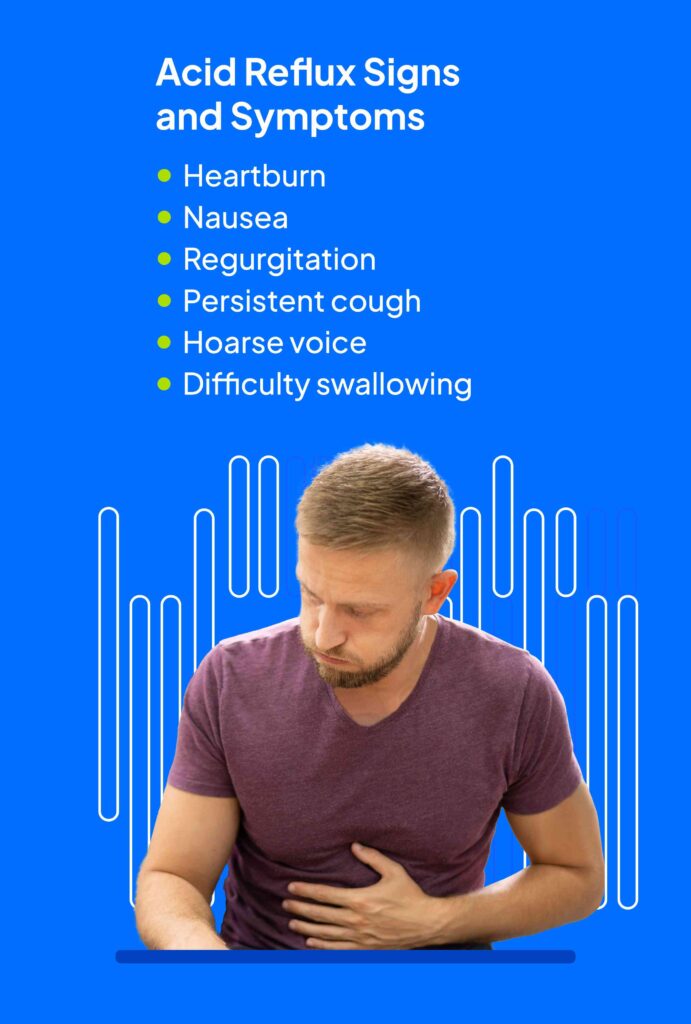
This image is property of www.health.com.
Potential Complications of Acid Reflux
When left untreated or unmanaged, acid reflux can lead to various complications. These complications may include:
Esophagitis
Chronic acid reflux can cause inflammation of the esophagus, a condition known as esophagitis. This can lead to symptoms such as pain, difficulty swallowing, and an increased risk of developing more serious conditions.
Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus is a condition in which the normal lining of the esophagus is replaced by abnormal cells. This change in the lining of the esophagus is associated with an increased risk of developing esophageal cancer.
Esophageal Stricture
Repeated exposure to stomach acid can cause the esophagus to become narrowed and constricted, leading to difficulty swallowing and an increased risk of food getting stuck.
Respiratory Issues
Acid reflux can cause or exacerbate respiratory issues such as asthma, chronic cough, and recurrent respiratory infections. The acid irritates the airways and can lead to breathing difficulties.
Esophageal Cancer
Long-term, untreated acid reflux can increase the risk of developing esophageal cancer. It is important to seek medical attention if you have persistent symptoms or concerns.
When to See a Doctor for Children
Acid reflux can affect individuals of all ages, including children. It is important for parents and caretakers to recognize the signs that indicate a need for medical evaluation.
Infants and Acid Reflux
Acid reflux is common in infants and is often referred to as gastroesophageal reflux (GER). Most infants outgrow this condition by the time they reach one year of age. However, it is recommended to seek medical attention if your infant shows signs of poor weight gain, persistent irritability, or feeding difficulties.
Symptoms in Children
In older children, acid reflux may present with symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, stomach pain, difficulty swallowing, or a chronic cough. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Importance of Medical Evaluation
For children with persistent or severe symptoms, medical evaluation is crucial to identify the underlying cause of acid reflux and determine the most appropriate treatment options. It is important not to dismiss or ignore acid reflux symptoms in children, as they can negatively impact growth and overall well-being.
Child-Friendly Treatment Options
Treatment options for acid reflux in children may include lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, medications, and in some cases, surgery. Healthcare professionals will take into consideration the age, severity, and specific needs of the child when developing a treatment plan.
This image is property of www.verywellhealth.com.
Preparing for a Doctor’s Appointment
When scheduling a doctor’s appointment for acid reflux, it can be helpful to gather pertinent information to ensure an effective evaluation. Taking the following steps can help maximize the value of the appointment:
Keeping a Symptom Diary
Keeping a symptom diary documenting the frequency, severity, and duration of acid reflux symptoms can provide valuable information to the healthcare provider. Include details about meals, triggers, and any factors that seem to worsen or alleviate symptoms.
Listing Medications and Lifestyle Factors
Make a list of all medications, including over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies. Discuss current lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, smoking, and alcohol consumption, as these can play a role in acid reflux.
Preparing Questions
Prepare a list of questions or concerns to discuss with the healthcare provider. This may include inquiries about treatment options, potential complications, and strategies for managing acid reflux.
Your doctor is there to help guide you and provide the best care possible, so it is important to be open and honest about your symptoms and concerns.
Choosing the Right Doctor
When seeking medical help for acid reflux, it is important to choose a healthcare professional who is experienced in diagnosing and treating digestive disorders. Two types of doctors commonly involved in the management of acid reflux are primary care physicians and gastroenterologists.
Primary Care Physician
A primary care physician is a general practitioner who can provide initial evaluation and management of acid reflux. They can assess symptoms, recommend lifestyle modifications, and prescribe medications. If further evaluation or specialized care is needed, they may refer you to a gastroenterologist.
Gastroenterologist
A gastroenterologist is a specialist who focuses on disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including acid reflux. They have extensive knowledge and experience in diagnosing and treating digestive disorders. Gastroenterologists may perform diagnostic tests, provide specialized treatment options, and monitor for potential complications.
Choosing the right doctor for your acid reflux management is crucial in ensuring appropriate care and achieving the best possible outcomes.
Conclusion
Acid reflux is a common digestive disorder that can cause discomfort and interfere with daily life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential in effectively managing this condition. While self-treatment can be appropriate for mild and occasional symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention if symptoms persist, worsen, or are accompanied by warning signs. With proper evaluation, diagnosis, and ongoing management, individuals with acid reflux can find relief and improve their quality of life. Remember, always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.