If you find yourself constantly experiencing heartburn or a burning sensation in your chest after meals, it may be time to consult a gastroenterologist for acid reflux. Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), can be a bothersome condition that affects many individuals. This article will discuss the common symptoms of acid reflux and provide guidance on when it is necessary to seek specialized medical care. So, keep reading to learn when to consult a gastroenterologist for acid reflux.
Understanding Acid Reflux
Definition of Acid Reflux
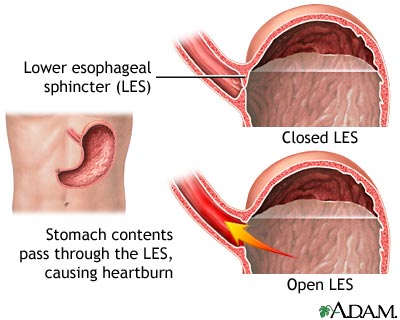
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a condition in which the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is a muscular ring that acts as a valve between the esophagus and the stomach. When the LES is weakened or relaxes inappropriately, it allows stomach acid to flow upward, causing irritation and inflammation of the esophageal lining.
Causes of Acid Reflux
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of acid reflux. Common causes include:
- Hiatal Hernia: A hiatal hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, which can weaken the LES and promote acid reflux.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put pressure on the abdomen, leading to the relaxation of the LES and an increased risk of acid reflux.
- Certain Foods and Beverages: Spicy foods, citrus fruits, fatty meals, caffeine, alcohol, and carbonated beverages are known triggers for acid reflux.
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the LES and increases stomach acid production, making individuals more susceptible to acid reflux.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can relax the LES, causing acid reflux symptoms.
Symptoms of Acid Reflux
The symptoms of acid reflux can vary from person to person, but common signs and symptoms include:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest that may radiate to the throat. It is often triggered by lying down or bending over after a meal.
- Regurgitation: A bitter or sour taste in the mouth due to the backflow of stomach acid into the throat or mouth.
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing or the sensation of food getting stuck in the throat.
- Chronic Cough: A persistent cough that is not related to a respiratory infection, often worse at night.
- Hoarseness: Changes in voice, such as a raspy or hoarse voice, may indicate acid reflux affecting the vocal cords.
Initial Self-Care Measures
Lifestyle Changes
Implementing certain lifestyle changes can help manage and reduce the symptoms of acid reflux. Consider the following measures:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight can alleviate pressure on the abdomen, reducing the risk of acid reflux.
- Elevate the Head of the Bed: Keep the upper body elevated while sleeping to help gravity keep stomach acid down.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Identify and avoid foods and beverages that trigger or worsen your acid reflux symptoms.
- Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals: Consuming smaller meals throughout the day can help prevent excessive stomach acid production.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking weakens the LES and worsens acid reflux symptoms, so quitting smoking is highly recommended.
Dietary Modifications
In addition to avoiding trigger foods, certain dietary modifications can help manage acid reflux symptoms effectively. Consider the following tips:
- Choose Non-Acidic Fruits: Opt for fruits such as bananas, melons, and apples, which are less likely to trigger acid reflux.
- Avoid Deep-Fried and Fatty Foods: These foods can relax the LES and delay stomach emptying, increasing the risk of acid reflux.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both caffeine and alcohol can stimulate excess stomach acid production and relax the LES, leading to acid reflux.
- Eat Slowly and Chew Thoroughly: This helps ensure proper digestion and reduces the likelihood of acid reflux symptoms.
- Avoid Eating Close to Bedtime: Allow at least two to three hours for digestion before lying down to allow gravity to aid the movement of stomach acid.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications can provide temporary relief from acid reflux symptoms. Some common OTC options include:
- Antacids: Antacids neutralize stomach acid and provide short-term relief from heartburn and indigestion.
- H2 Blockers: Histamine-2 (H2) blockers reduce the production of stomach acid and can be taken before consuming trigger foods.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs reduce the production of stomach acid and may provide longer-lasting relief when taken regularly.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any OTC medications to ensure proper usage and safety.
This image is property of www.thenewtownclinic.in.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Frequent Occurrence of Symptoms
If you experience acid reflux symptoms more than twice a week, it is advisable to seek medical advice. Frequent occurrence of symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires medical intervention.
Symptoms Persist Despite Lifestyle Changes
If you have made lifestyle modifications and followed self-care measures, but your acid reflux symptoms persist or worsen, it is recommended to consult a gastroenterologist. They can evaluate your condition and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Chest Pain or Difficulty Swallowing
Severe chest pain or difficulty swallowing can be signs of complications associated with acid reflux, such as esophagitis or Barrett’s esophagus. These symptoms warrant immediate medical attention and evaluation.
Unintentional Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss can be a concerning symptom and may indicate a more serious underlying condition. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause.
Severe Heartburn at Night
If you experience severe heartburn that disrupts your sleep or occurs predominantly at night, it could be a sign of severe acid reflux. Seeking medical advice can help identify the cause and provide appropriate treatment.
Persistent Cough or Hoarseness
If you have a persistent cough or experience voice changes, such as hoarseness, it may be indicative of acid reflux affecting the throat and vocal cords. Consultation with a gastroenterologist is recommended for proper evaluation and management.
Worsening Symptoms
If your acid reflux symptoms are worsening or becoming more frequent over time, it is important to seek medical advice. This may indicate a progression of the condition or the need for a change in treatment approach.
The Role of a Gastroenterologist
Education and Expertise
Gastroenterologists are medical specialists who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting the digestive system, including acid reflux. Their extensive education and expertise equip them with the knowledge and skills to provide comprehensive care for individuals with acid reflux.
Specialized Diagnostic Tools
Gastroenterologists have access to specialized diagnostic tools and procedures that can aid in the accurate diagnosis of acid reflux. These may include:
- Upper Endoscopy: A procedure that involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera through the mouth to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
- Esophageal pH Monitoring: A test that measures the pH level in the esophagus over 24-48 hours to assess the frequency and severity of acid reflux episodes.
- Barium Swallow X-ray: A series of X-rays taken after swallowing a liquid containing barium, which coats the esophagus and helps detect abnormalities.
- Manometry: A procedure that measures the pressure and coordination of the muscles in the esophagus to assess its function and detect any abnormalities.
Advanced Treatment Options
Gastroenterologists are well-versed in the latest treatment options for acid reflux. They can provide individualized treatment plans based on the severity of symptoms, underlying causes, and the patient’s overall health. Advanced treatment options may include:
- Endoscopic Treatments: Minimally invasive procedures performed through an endoscope to treat conditions such as hiatal hernias or repair the LES.
- LINX Reflux Management System: A small ring of magnetic beads placed around the lower esophagus to help strengthen the LES and prevent acid reflux.
- Anti-reflux Surgery: In severe cases or when other treatments have failed, surgical intervention may be necessary to reinforce the LES or repair hernias.

This image is property of gidoc.co.za.
Diagnosing Acid Reflux
Medical History and Physical Examination
A medical history and physical examination are typically the first steps in diagnosing acid reflux. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and may perform a physical examination to assess for signs of acid reflux.
Upper Endoscopy
An upper endoscopy may be recommended to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. During the procedure, a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to identify any abnormalities or signs of inflammation.
Esophageal pH Monitoring
Esophageal pH monitoring involves placing a small catheter through the nose or mouth into the esophagus to measure the pH level and monitor acid reflux episodes over 24-48 hours. This test helps assess the frequency and severity of acid reflux.
Barium Swallow X-ray
A barium swallow X-ray is a diagnostic test in which the patient drinks a liquid containing barium, which coats the esophagus, allowing abnormalities to be detected on X-ray images. This test can help identify hernias, strictures, or other structural issues.
Manometry
Manometry is a procedure that measures the pressures and coordination of the muscles in the esophagus. It helps evaluate the function of the esophagus and detect any abnormalities that may be contributing to acid reflux symptoms.
Treatment Approaches
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing acid reflux. Along with the initial self-care measures mentioned earlier, additional lifestyle changes may include:
- Avoiding tight-fitting clothing: Wearing loose-fitting clothing can reduce pressure on the abdomen and LES.
- Stress management: Finding effective stress management techniques, such as meditation or exercise, can minimize acid reflux symptoms.
- Elevating the head of the bed: Sleeping with the upper body elevated can help prevent acid reflux at night.
- Not lying down immediately after a meal: Allowing sufficient time for digestion before lying down can reduce acid reflux symptoms.
Medications
Medications can help alleviate acid reflux symptoms and promote healing of the esophagus. Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): These medications reduce the production of stomach acid and provide long-term relief from acid reflux symptoms.
- H2 Blockers: H2 blockers decrease the production of stomach acid and can be used as an alternative to PPIs.
- Antacids: Over-the-counter antacids can provide temporary relief by neutralizing stomach acid.
- Prokinetics: Prokinetic medications help improve the movement of food through the digestive system, reducing the likelihood of acid reflux.
Surgical Intervention
In cases where lifestyle modifications and medications fail to sufficiently manage acid reflux, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgical options for acid reflux include:
- Fundoplication: This procedure involves wrapping the upper part of the stomach around the LES to reinforce its function and prevent acid reflux.
- LINX Reflux Management System: The LINX device, a ring of magnetic beads, is implanted around the lower esophagus to strengthen the LES and reduce acid reflux occurrences.
- Endoscopic Treatments: Minimally invasive procedures using an endoscope can be performed to repair the LES or hernias causing acid reflux.
This image is property of images.squarespace-cdn.com.
Complications and Risks
Esophagitis
Esophagitis refers to inflammation or irritation of the lining of the esophagus. If left untreated, chronic acid reflux can lead to esophagitis, which may cause pain, difficulty swallowing, and complications such as bleeding or ulcers.
Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus is a condition characterized by changes in the lining of the esophagus due to long-term acid exposure. It increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer, so regular monitoring and treatment by a gastroenterologist are essential.
Esophageal Stricture
Chronic acid reflux can cause narrowing of the esophagus, leading to difficulty swallowing or a feeling of food getting stuck. This is known as an esophageal stricture and may require interventions such as dilation to alleviate symptoms.
Respiratory Issues
Acid reflux can also result in respiratory problems, such as coughing, wheezing, or recurring episodes of pneumonia. This occurs when stomach acid reaches the throat and lungs, irritating the airways and causing respiratory symptoms.
Special Considerations
Pediatric Acid Reflux
Acid reflux can occur in infants and children as well. Parents should be aware of the signs and symptoms, such as frequent spitting up, fussiness during or after feeding, and poor weight gain. Consulting a pediatric gastroenterologist is recommended for proper evaluation and management.
Pregnancy and Acid Reflux
Pregnant women often experience acid reflux due to hormonal changes and the growing uterus putting pressure on the stomach. Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider for safe and effective treatment options.
Elderly Patients
Older adults may be more prone to developing acid reflux due to age-related changes in the esophagus and the presence of other medical conditions. Appropriate management and regular monitoring by a gastroenterologist are crucial for elderly individuals.
This image is property of wakegastro.com.
When to Consult a Gastroenterologist
Persistent or Severe Symptoms
If your acid reflux symptoms persist or worsen despite initial self-care measures and over-the-counter medications, it is advisable to consult a gastroenterologist. They can assess your condition, determine the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Suspected Complications
If you experience symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty swallowing, persistent cough, or unintentional weight loss, it may indicate complications related to acid reflux. Seeking medical advice can help evaluate and manage these complications effectively.
Unresponsiveness to Initial Treatments
If your acid reflux symptoms do not improve with lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and over-the-counter medications, it is important to consult a gastroenterologist. They can provide a thorough evaluation and recommend alternative treatment options.
Need for Specialized Diagnostic Procedures
If your healthcare provider suspects complications or needs more detailed information about your acid reflux, they may refer you to a gastroenterologist for specialized diagnostic procedures such as endoscopy or pH monitoring.
Seeking Expert Medical Opinion
If you are unsure about the severity of your acid reflux symptoms or have concerns about your condition, seeking expert medical opinion from a gastroenterologist can provide reassurance and peace of mind. They can address your questions and provide personalized advice.
Preparing for a Gastroenterology Appointment
Keeping a Symptom Diary
Before your gastroenterology appointment, it may be helpful to keep a symptom diary to track the frequency, duration, and severity of your acid reflux symptoms. This can provide valuable information to your healthcare provider and facilitate an accurate diagnosis.
Preparing Relevant Questions
Make a list of any questions or concerns you have about your acid reflux. These can include questions about treatment options, potential risks, lifestyle modifications, and any specific worries you may have. This will ensure that you address all your concerns during your appointment.
Medical Records and Reports
Bring any relevant medical records, test results, or reports related to your acid reflux to your appointment. This will help the gastroenterologist better understand your medical history and aid in the diagnosis and treatment process.
Medication List
Compile a list of all the medications you are currently taking, including OTC medications and any supplements. This will ensure that your gastroenterologist has a complete overview of your medical regimen and can make appropriate recommendations.
Insurance and Cost Considerations
If you have specific insurance coverage or cost considerations, it is important to discuss them with your healthcare provider and gastroenterologist. They can guide you in choosing the most appropriate diagnostic tests and treatment options that align with your insurance coverage and budget.
In conclusion, understanding acid reflux is essential for effectively managing this condition. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and seeking appropriate medical advice, individuals can find relief from the discomfort of acid reflux and reduce the risk of complications. Consultation with a gastroenterologist can provide expert guidance, advanced diagnostic tools, and specialized treatment options tailored to the individual’s needs. With proper care and lifestyle modifications, individuals can regain control of their digestive health and improve their overall wellbeing.

This image is property of drssabnis.com.

